Abstract
Introduction: standard treatment for relapsed/refractory (R/R) diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is high-dose chemotherapy followed by autologous stem-cell transplantation (ASCT) but this strategy is not appropriate for elderly DLBCL patients (pts) related to a high risk of toxicities. Multiple chemotherapy regimens had been developed for heavily pretreated elderly DLBCL patients such as R-bendamustine, R-gemcitabine-oxaliplatin (R-GEMOX) and pixantrone; the median progression free survival (PFS) of these regimens were 2, 4 and 3.5 months, respectively in prospective phase II studies for patients previously treated with R (Sehn 2017, Mounier 2013, Pettengel 2016). Adapted dose of ifosfamide and etoposide was firstly developed as sequential consolidation regimen after high-dose CHOP (ACVBP regimen) in first line therapy of young DLBCL patients (Tilly 2003). This regimen with a safe toxicity profile was then used in combination with R in Lyon University Hospital in elderly R/R DLBCL ineligible to intensive strategy.
Methods: we retrospectively reviewed the efficacy and the safety profile of this regimen performed in two Lyon University Hospitals (Centre Hospitalier Lyon Sud and Leon Berard Cancer Center). Between June 2004 and March 2017, 75 pts with R/R DLBCL (63 de novo DLBCL, 12 transformed DLBCL) received R (375 mg/m2) in combination etoposide (300 mg/m2) and ifosfamide (1500 mg/m2) on day 1 (N=72, 96%) and on days 1-2 (N=3, 4%) at 2 (N=46, 61%) or 3-week (N=29, 39%) intervals. All medical records were reviewed for clinical and biological characteristics, modality of treatment and supportive care, toxicities, responses and outcome.
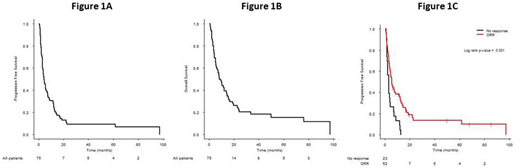
Results: the median age was 79 years (range, 64-92) at the beginning of R-ifosfamide/VP16 treatment with 46% of the patients over 80 years. 13% of pts had a CIRS-G grade 3 or 4 >2 categories and 35% had a cumulative CIRS-G score more than 6. The performance status according to EORTC scale was 2-4 in 37% of the pts and 93% had III-IV Ann Arbor stages. Age-adjusted IPI were 0-1 in 20 pts (27%) and 2-3 in 55 pts (73%). All patients were previously treated in first-line therapy by R in combination with chemotherapy (CHOP, N=56, 75%, low-dose CHOP, N=14, 19%, other, N=5, 6%). The patients received a median number of 1 previous line (range, 1-8) and no patient was previously treated by ASCT. The median time between initial diagnosis and R-ifosfamide/VP16 was 20 months (range 4-187). The median time between the last treatment and R-ifosfamide/VP16 was 5 months (range 0-181). A refractory disease to first-line treatment was showed in 14 pts (19%). 31% of the patients had a refractory disease to the last regimen performed before R-ifosfamide/VP16. Patients received a median of 6 cycles (1-12). At the end of treatment, the overall response rate (ORR), defined by the rate of complete response (CR) and partial response (PR) was 37%, with 18% of CR. Evaluations were assessed for 29% of the pts by TEP scanner. For toxicity, among the 387 cycles, 10 patients developed febrile neutropenia (2.6%); 15 (20%) a grade 3-4 neutropenia; 7 (9%) a grade 3-4 thrombocytopenia; 5 patients needed platelet units and 16 patients received packed red blood cell units. No grade 3-4 non-hematological toxicity was observed and no toxic death occurred. With a median follow up of 31.3 months (range, 5.0-202.8), the median progression-free survival (PFS) was 4.3 months with a 1-year PFS rate of 26.0% (95%CI, 17.7-38.3) (Figure 1A). The median overall survival (OS) was 8.2 months with a 1-year OS rate of 40.8% (95%CI, 30.9-54.0) (Figure 1B). The median duration of response was 4 months (range 1-97). The median PFS was adversely affected by response (refractory versus CR/PR) to the last treatment (3.0 months versus 5.5 months, P=0.001) (Figure 1C).
Conclusions: in this retrospective study, R-Ifosfamide/VP16 regimen provided effective results in R/R DLBCL transplant-ineligible pts with 37% of ORR and a median of PFS of 4.3 months with a safe toxicity profile. This regimen could also be considered as a platform for combinations with novel targeted agents in these categories of patients.
Karlin:Amgen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: travel support; Janssen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: travel support; Celgene: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Sarkozy:ROCHE: Consultancy. Bachy:Gilead Sciences: Honoraria; Takeda: Research Funding; Sandoz: Consultancy; Amgen: Honoraria; Roche: Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy; Janssen: Honoraria. Salles:Abbvie: Honoraria; Epizyme: Honoraria; Amgen: Honoraria; F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Gilead: Honoraria, Other: Advisory Board; Acerta: Honoraria; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria; Servier: Honoraria; Servier: Honoraria, Other: Advisory Board; Takeda: Honoraria; BMS: Honoraria, Other: Advisory Board; Celgene: Honoraria, Other: Advisory Board, Research Funding; Janssen: Honoraria, Other: Advisory Board; Merck: Honoraria; Morphosys: Honoraria; Pfizer: Honoraria. Ghesquieres:Sanofi: Consultancy; Gilead: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal